Fibula or Ankle Fracture: Diagnosis and Treatment with Dr. Ramadan Ahmed
Published on: 2025-06-28 | Written by: Dr. Ramadan Ahmed Ramadan, Orthopedic Surgery
Fibula or ankle fractures are common injuries caused by falls or sudden twisting of the foot, especially among athletes and the elderly.
Dr. Ramadan Ahmed Ramadan, Consultant in Orthopedic Surgery, explains that accurate diagnosis and assessment of fracture severity are key to choosing the proper treatment plan—whether conservative or surgical.
What Is the Fibula and Where Is It Located?
The fibula is one of the two bones in the lower leg (alongside the tibia), running from the knee to the ankle on the outer side.
A fracture may occur on its own or in combination with an ankle or ligament injury. Dr. Ramadan Ahmed Ramadan notes that some fractures are minor, while others significantly affect ankle joint stability.
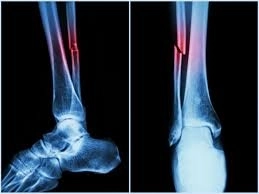
How Is the Fracture Diagnosed?
Dr. Ramadan Ahmed Ramadan relies on several tools to diagnose the fracture:
-
Clinical examination to identify pain location and swelling
-
X-rays to assess the position and extent of the fracture
-
CT or MRI scans in some cases to check for ligament damage or joint involvement
What Are the Available Treatment Options?
According to Dr. Ramadan Ahmed Ramadan, treatment depends on the location and severity of the fracture and may include:
-
Conservative treatment: Using a splint or cast for simple, non-displaced fractures
-
Surgical intervention: In cases of bone displacement or joint involvement, using plates and screws to ensure proper alignment and healing
Is Rehabilitation Needed After Treatment?
Dr. Ramadan Ahmed Ramadan emphasizes the importance of physical rehabilitation to restore ankle movement and strengthen surrounding muscles after cast removal or surgery. This may include:
-
Exercises to improve range of motion
-
Muscle strengthening routines
-
Balance and gait training for safe walking
Conclusion
A fibula or ankle fracture requires thorough evaluation by a specialist to prevent long-term complications like joint stiffness or limited mobility.
Dr. Ramadan Ahmed Ramadan stresses that early diagnosis, accurate treatment, and guided rehabilitation are essential for full recovery and a return to normal activity.